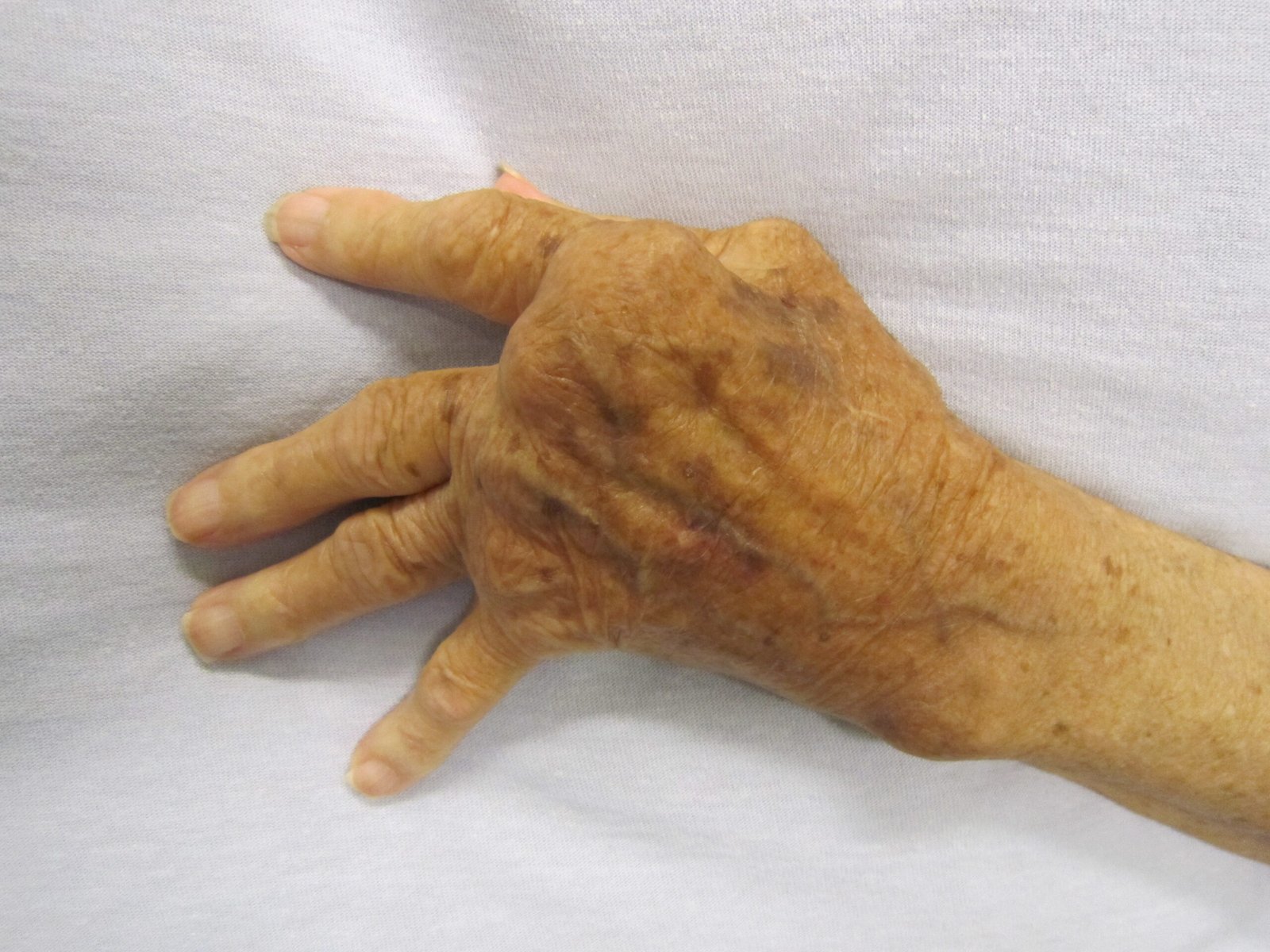
What is Arthritis?
Symptoms of Arthritis
The signs and symptoms of arthritis vary depending on the type but commonly include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling and tenderness in one or more joints
- Reduced range of motion
- Redness or warmth around the joints
- Fatigue and weakness
- Joint deformity in severe cases
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes (commonly seen in RA)
Causes & Risk Factors
- Age: Risk increases with age
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop RA; men more often develop gout
- Family history: Genetics can play a role
- Obesity: Extra weight puts more stress on joints
- Injuries: Joint injuries can lead to osteoarthritis later
- Infections or autoimmune disorders: Can trigger or worsen arthritis
Types of Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis (OA) – Degenerative joint disease due to cartilage breakdown
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Autoimmune disorder affecting joint lining
- Psoriatic Arthritis – Associated with psoriasis skin condition
- Gout – Caused by uric acid crystal buildup
- Ankylosing Spondylitis – Affects spine and pelvis
- Juvenile Arthritis – Affects children under 16
- Reactive Arthritis – Triggered by infections in other parts of the body
Diagnosis and Procedures
Diagnosing arthritis involves a combination of:
- Medical history and physical exam
- Blood tests (e.g., rheumatoid factor, ESR, CRP)
- Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, Ultrasound)
- Joint fluid analysis
Treatment Options for Arthritis
There is no permanent cure for most types of arthritis, but effective treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Medications:
Pain relievers (paracetamol, NSAIDs)
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for RA
Biologic response modifiers
Corticosteroids
2. Physical Therapy:
Tailored exercise programs
Strengthening and flexibility training
Assistive devices (braces, canes)
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
Weight management
Low-impact exercises (yoga, swimming)
Anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3, antioxidants
4. Surgical Options:
Joint replacement surgery (knee, hip)
Arthroscopy (removal of debris or repair)
Joint fusion
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all types of arthritis are preventable, you can significantly reduce your risk by:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Staying physically active
Avoiding joint injuries
Eating a balanced diet
Managing chronic diseases like diabetes or hypertension
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption
Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Management
- Reduces joint damage and deformities
- Preserves joint function and mobility
- Improves daily functioning and independence
- Minimizes pain and inflammation
- Enhances overall quality of life
