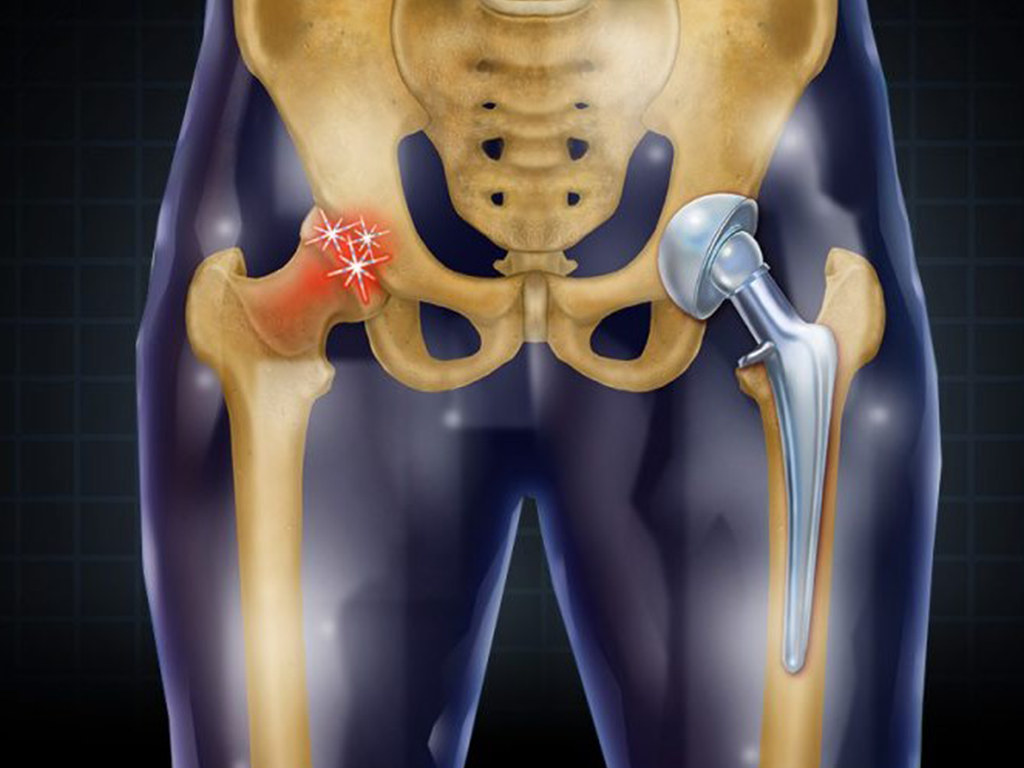
What is Hip Replacement?
Hip replacement, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or worn-out hip joint is replaced with an artificial implant (prosthesis). This surgery is typically recommended when chronic hip pain and stiffness interfere with daily activities and conservative treatments like medication and physical therapy fail to provide relief.
Hip replacement restores mobility, reduces pain, and significantly improves the quality of life for individuals suffering from severe hip conditions.our team of experienced orthopedic surgeons uses advanced surgical techniques and high-quality implants to ensure optimal outcomes. We offer personalized care, modern facilities, and comprehensive post-operative support to help you walk pain-free again.
Common Symptoms Indicating the Need for Hip Replacement
- Persistent pain in the hip or groin, especially while walking, standing, or climbing stairs
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion in the hip joint
- Difficulty in standing up from a seated position
- Limping or dragging of the leg
- Pain that interferes with sleep or daily routines
- Swelling or tenderness around the hip
If these symptoms are affecting your mobility and independence, it may be time to consider a hip replacement evaluation.
Causes of Hip Joint Dama
- Osteoarthritis – Age-related wear and tear of the joint cartilage
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – Inflammation of the joint lining
- Traumatic Injury – Fractures or dislocations due to accidents
- Avascular Necrosis – Loss of blood supply leading to bone collapse
- Congenital Hip Disorders – Abnormal development from birth
Hip Replacement Procedure
Hip replacement is generally performed under spinal or general anesthesia. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Incision – A cut is made over the hip to access the joint.
- Removal of Damaged Tissue – The damaged bone and cartilage are removed.
- Implantation – The prosthetic components (metal, ceramic, or plastic) are inserted to replace the ball-and-socket structure.
- Closure – The incision is closed, and the patient is moved to recovery.
Modern techniques such as minimally invasive surgery and robot-assisted hip replacement offer faster recovery and less post-operative discomfort.
Types of Hip Replacement
- Total Hip Replacement (THR) – Both the acetabulum (hip socket) and the femoral head are replaced.
- Partial Hip Replacement – Only the femoral head is replaced, often done in cases of hip fractures.
- Hip Resurfacing – The femoral head is capped with a metal covering instead of removing it entirely.
- Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement – Smaller incisions and less tissue damage, leading to quicker healing.
Benefits of Hip Replacement
- Significant relief from chronic pain
- Improved joint function and mobility
- Enhanced quality of life and ability to perform daily activities
- Long-lasting results – implants may last 15–20 years or more
- Reduced dependence on walking aids and pain medications
Prevention and Joint Care Tips
While not all hip conditions are preventable, the following tips can reduce the risk of joint damage:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Exercise regularly to keep joints flexible and muscles strong
- Avoid high-impact activities if prone to joint issues
- Take steps to prevent falls and injuries
- Treat joint-related conditions early to delay or avoid surgery
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-surgery, patients typically undergo physical therapy to regain strength, balance, and mobility. Full recovery can take a few weeks to several months, depending on the individual and the type of surgery. Following your surgeon’s advice, doing regular physiotherapy, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key to long-term success.
