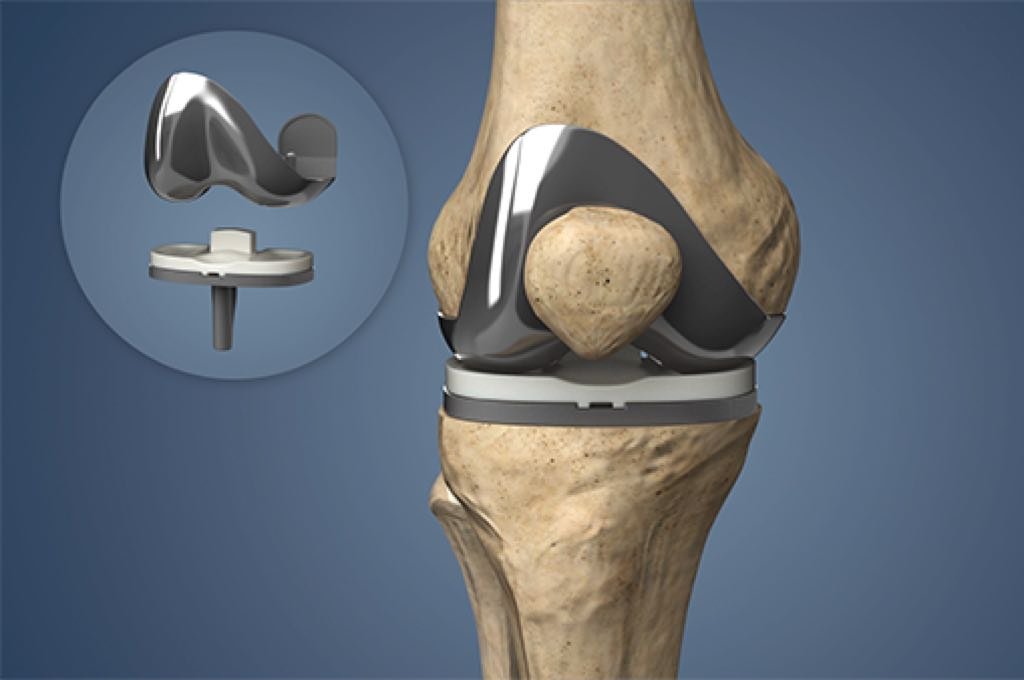
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure in which a damaged or diseased knee joint is replaced with an artificial implant (prosthesis). It is commonly recommended for individuals suffering from severe arthritis, chronic knee pain, or joint damage that limits daily activities and affects quality of life. This surgery is designed to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve joint function.Knee replacement surgery is a safe and effective solution for individuals suffering from debilitating knee joint pain and damage. If conservative treatments like medication, lifestyle changes, and physical therapy have not brought relief, knee replacement may restore your comfort and independence.
Symptoms That May Require Knee Replacement
You may need to consult an orthopedic specialist for knee replacement if you experience the following symptoms:
- Persistent knee pain that doesn’t respond to medication or therapy
- Swelling and stiffness in the knee joint
- Difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or standing from a seated position
- Pain while resting, especially at night
- Bowing or deformity of the knee
- Limited range of motion
These symptoms are commonly seen in conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis.
Knee Replacement Procedure
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-surgical Assessment: Includes physical examination, imaging tests (X-rays or MRI), and blood tests to determine the extent of joint damage and overall health.
- Anesthesia: The surgery is usually done under spinal or general anesthesia.
- Joint Replacement: The surgeon removes the damaged portions of the thighbone (femur), shinbone (tibia), and kneecap (patella), then replaces them with metal or plastic components.
- Closure and Recovery: The incision is closed, and the patient is shifted to recovery. Rehabilitation begins soon after surgery with physiotherapy to restore movement and strength.
The surgery usually takes 1 to 2 hours, and patients often begin walking with assistance within a day or two.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
Depending on the severity of the damage and patient needs, different types of knee replacement may be performed:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Most common type where the entire joint surface is replaced with a prosthesis.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): Only the damaged part of the knee is replaced; suitable for localized arthritis.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement: Both knees are replaced simultaneously or in staged procedures.
- Revision Knee Replacement: Performed if the previous knee implant fails or wears out.
Prevention and Risk Management
While not all cases of knee degeneration can be prevented, you can lower your risk of needing knee replacement by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Staying active and strengthening leg muscles
- Avoiding injuries through proper technique during sports or physical activity
- Managing arthritis with early diagnosis, medications, and physiotherapy
- Using supportive footwear and joint protection techniques
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Long-lasting relief from chronic knee pain
- Improved mobility and quality of life
- Better joint alignment and functionality
- Enhanced ability to participate in everyday activities and low-impact sports
- High success rate and durability of implants (typically last 15-20 years)
