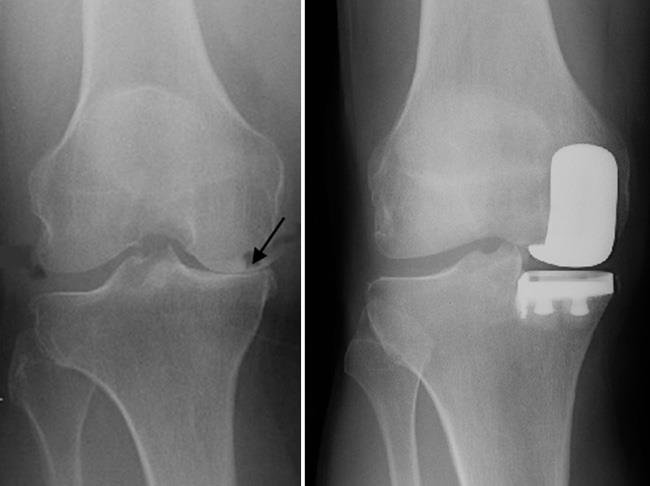
What is Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial Knee Replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat damage or arthritis in one part (compartment) of the knee. Unlike total knee replacement, where the entire joint is replaced, partial knee replacement involves replacing only the affected area, preserving healthy bone, cartilage, and ligaments.
This procedure is ideal for patients who have osteoarthritis confined to a single compartment of the knee—either the inner (medial), outer (lateral), or the kneecap (patellofemoral).
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Partial Knee Replacement
If you’re experiencing the following symptoms, you might be a candidate for partial knee replacement:
- Persistent knee pain localized to one side
- Swelling or inflammation in the affected compartment
- Limited mobility or stiffness
- Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or standing for long periods
- Pain that doesn’t respond well to medications or physiotherapy
- Bow-legged or knock-kneed deformity
Procedure & Treatment
The partial knee replacement procedure typically involves the following steps:
Diagnosis & Imaging: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans confirm if the damage is limited to one knee compartment.
Anesthesia: The patient is given regional or general anesthesia.
Surgical Process:
A small incision is made to access the damaged area.
The worn-out cartilage and bone are removed.
A metal or plastic implant is fixed to the area to restore joint movement.
Recovery: Most patients are encouraged to start walking with support on the same or next day. Physical therapy begins immediately to regain strength and motion.
Prevention of Knee Joint Degeneration
Although arthritis and wear-and-tear can be age-related, you can take preventive steps to reduce the risk of knee joint damage:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Stay active with low-impact exercises (swimming, cycling, yoga)
- Use proper techniques when lifting or exercising
- Wear supportive footwear
- Manage conditions like diabetes and osteoporosis effectively
- Regular physiotherapy or check-ups if you have early signs of knee problems
Benefits of Partial Knee Replacement
- Less Invasive: Smaller incision and quicker healing
- Preservation of Healthy Tissue: Only the damaged compartment is treated
- Faster Recovery: Shorter hospital stay and quicker return to daily activities
- Improved Knee Function: Restores mobility with natural knee movement
- Lower Blood Loss and reduced risk of complications compared to total knee replacement
- Long-Term Relief from pain and stiffness
Types of Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement is categorized based on the compartment treated:
- Medial Unicompartmental Replacement
– Most common type; addresses damage to the inner side of the knee. - Lateral Unicompartmental Replacement
– Performed when damage is on the outer side of the knee. - Patellofemoral Replacement
– Suitable when only the kneecap and its groove are affected.
